Transforming Financial Ecosystems
Introduction to Open Banking
Open banking transforms financial services by enabling seamless and secure interactions between banks and third-party providers. This innovative framework supports faster, more transparent, and efficient financial transactions, fostering customer-centric ecosystems.
At its core, open banking empowers users to securely share their financial data while enabling institutions to provide real-time services, especially in regions like the EU and Gulf areas.
By leveraging modern architectural standards like OAuth 2.0 and Financial Grade APIs (FAPI), open banking ensures robust data protection and interoperability.


How we can help?
What does Open Banking aim to?
Encourage Competition
Drive innovation by creating a level playing field for financial service providers.
Enhance Transparency
Provide customers with a consolidated view of their financial products.
Empower Users
Grant customers control over their data, including authorization to share it with third parties.
Our financial services
Open banking transforms financial services by enabling seamless and secure interactions between banks and third-party providers.

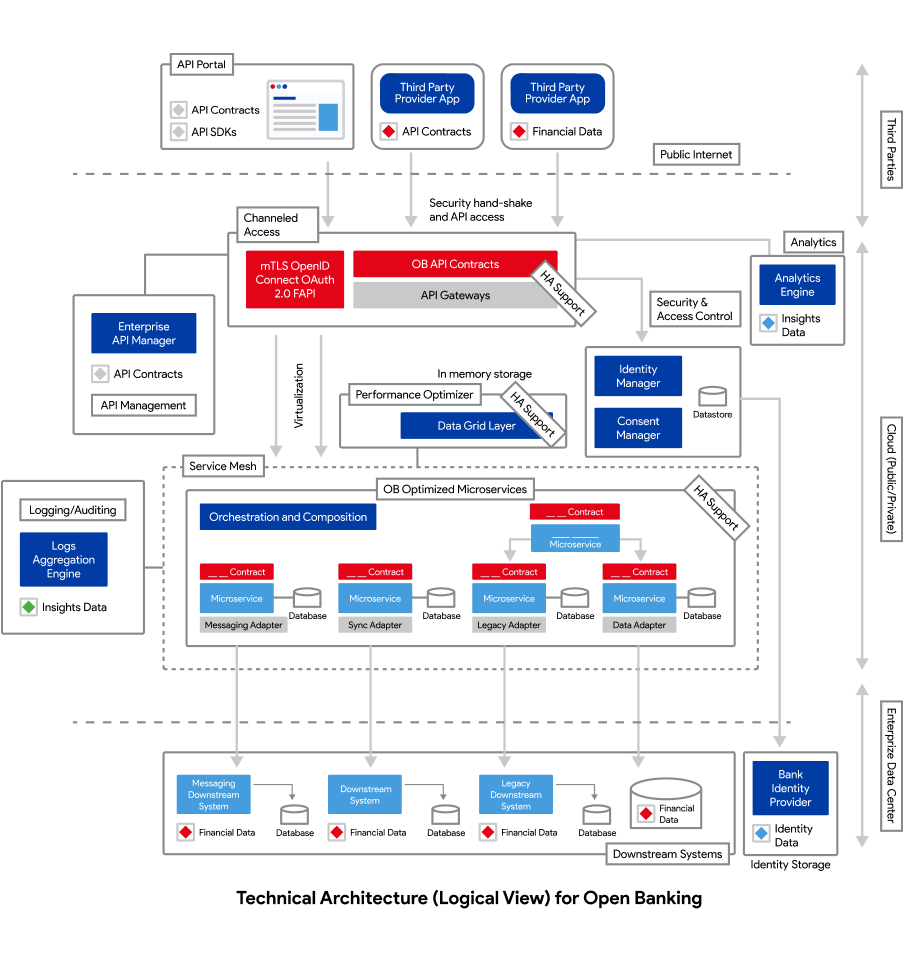
Core Components of Open Banking Architecture
The following diagram represents the logical structure of an open banking ecosystem. It illustrates how core components such as the API Gateway, microservices, consent manager, and orchestration layers interact to facilitate secure communication between banks, third-party providers, and end-users. This architecture ensures seamless integration while maintaining compliance and data integrity.
OAuth in Open Banking
OAuth 2.0 is the foundation of secure authorization in open banking. However, open banking builds on it with additional specifications to meet stringent financial sector requirements.
By incorporating Financial Grade APIs and mTLS (mutual Transport Layer Security), open banking ensures trust, compliance, and secure data sharing among all parties.
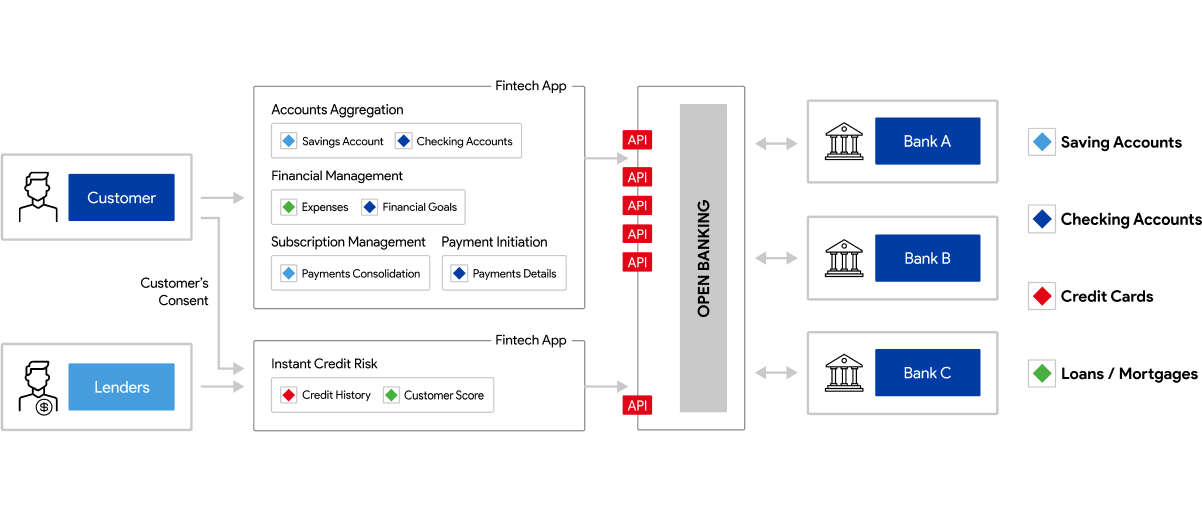
High security
OAuth 2.0 is the foundation of secure authorization in open banking.

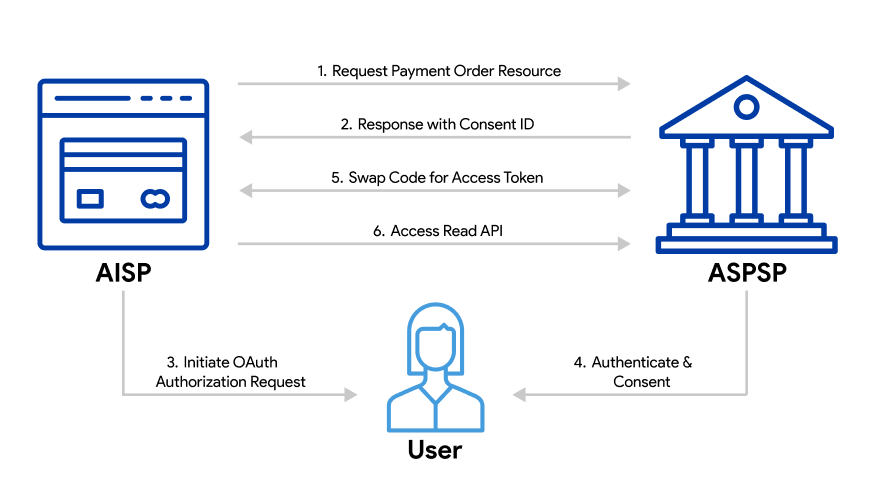
Account Information Service Providers (AISPs)
AISPs are services that access read-only financial data, such as account balances or transaction history, to provide value-added services like budgeting tools or account aggregators.
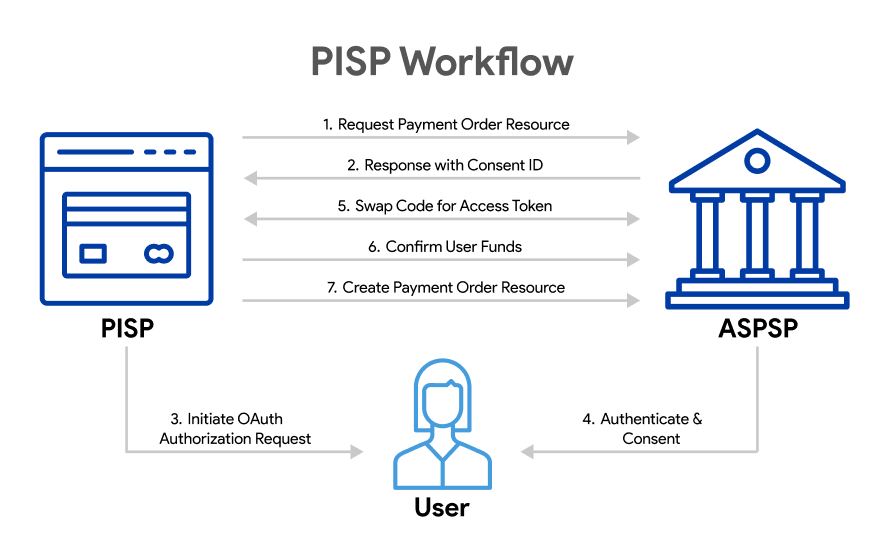
Payment Initiation Service Providers (PISPs)
PISPs are services that allow users to initiate payments directly from their bank accounts, providing a faster, more cost-effective alternative to traditional card-based payment systems.
Key Features of Open Banking
OAuth 2.0 is the foundation of secure authorization in open banking. However, open banking builds on it with additional specifications to meet stringent financial sector requirements.

Streamlined Data Sharing
- Banks and authorized third parties share data securely through APIs.
Enables customers to access services like account aggregation and budgeting tools.
Efficient Payment Solutions
- Direct account-to-account payments reduce transaction fees and processing times.
- Supports innovative services like one-click payments and subscription management.


Enhanced User Control
- Transparent consent flows ensure users have complete control over their data and transactions.
- Real-time insights help customers make better financial decisions.
Open banking creates a secure, transparent, and user-centric ecosystem for financial services. By leveraging microservices, OAuth 2.0, and FAPI, banks and third-party providers can deliver innovative services that meet modern financial needs. These workflows, backed by robust security measures, ensure the integrity of data sharing and payment processing while empowering customers to control their financial journey.
